 Illusion news 15
Illusion news 15 
 Illusion news 15
Illusion news 15 
since April 25, 2011
The website of Illusion Contest in Japan has been opened!
cf. The website of Best Illusion of the Year Contest
<December 31, 2012>
 The Okuma illusion: a new illusion of leaning
The Okuma illusion: a new illusion of leaning
Yasuda T, Ueda T, Shiina K, 2012, "The Okuma illusion: a new illusion
of leaning" Perception 41(10) 1277 – 1280
(First prize of the 3rd Illusion Contest in Japan)
<December 21, 2012>
Correction to a report in Illusion News 6
Thanks to Jasmina
<December 22, 2012>
--- The original is shown below ---
The Ebbinghaus illusion may be Ebbinghaus' illusion!
<August 25, 2007>
Wundt (1898, Fig. 49) cited this image as Ebbinghaus' figure. Kitaoka (2005), however, inferred that the first scholar who produced this illusion (= Ebbinghaus size illusion, Ebbinghaus areal illusion, Titchener illusion, Titchener circle, etc.) might be in fact Lipps, since the figure is found (without reference) in a monograph by Lipps (1897, p. 222), a year before Wundt's monograph and also earlier than the textbooks by Ebbinghaus (1902) or Titchener (1901). Recently, Walter H. Ehrenstein, University of Dortmund, found that Thiéry showed this image with explicit reference to Ebbinghaus even earlier (Thiéry, 1896, pp. 84-85; Figs. 51A and 51B). Thus, it is strongly suggested that the above figure has indeed originated with Ebbinghaus as had been suggested before by Ehrenstein & Hamada (1995, p. 158), based on Wundt’s (1898) account. Below is Walter's opinion:
So I think, it is Ebbinghaus who first designed it and may have communicated his figure at a congress before 1896 (rather than publish it, although this might be still the case, at that time the scientific world was quite small and people knew the work of each other even without explicit reference).
References
Ebbinghaus, H. (1902) Grundzüge der Psychologie. Leipzig: Veit.
Ehrenstein, W.H. and Hamada, J. (1995) Structural factors of size contrast
in the Ebbinghaus illusion. Japanese Psychological Research, 37, 158-169.
Kitaoka, A. (2005) Geometrical illusions. In Goto, T. and Tanaka, H. (Eds.), Handbook of the Science of Visual Illusion, Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press (pp. 56-77).
Lipps, T. (1897) Raumästhetik und geometrisch-optische Täuschungen. Leipzig: Barth.
Thiéry, A. (1896) Über geometrisch-optische Täuschungen, Schluss. Philosophische Studien, 12, 67-126.
Titchener, E. B. (1901) Experimental Psychology: A Manual of Laboratory Practice, Volume I. New York: Macmillan.
Wundt, W. (1898) Die geometrisch-optischen Tãuschungen. Abhandlungen der Mathematisch-Physischen Classe der Sächsischen Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften, Leipzig, 24, 53-178.
Information of Theodor Lipps
Thanks to Jasmina
<December 21, 2012>
Information of Armand Thiéry
Thanks to Jasmina
<December 22, 2012>
Anstis, S. (2012) The furrow illusion: Peripheral motion becomes aligned with stationary contours. Journal of Vision, 12(12):12, 1–11.
<November 22, 2012>
Some of Akiyoshi Kitaoka's (北岡明佳) works has been exhibited in Hong Kong.
Christmas Illusion exhibition
Date: 17 Nov-2013, 6 Jan
Time:
10:00am-10:00pm
Venue: Kingswood Ginza Phase 1, Tin Shui Wai, Hong Kong
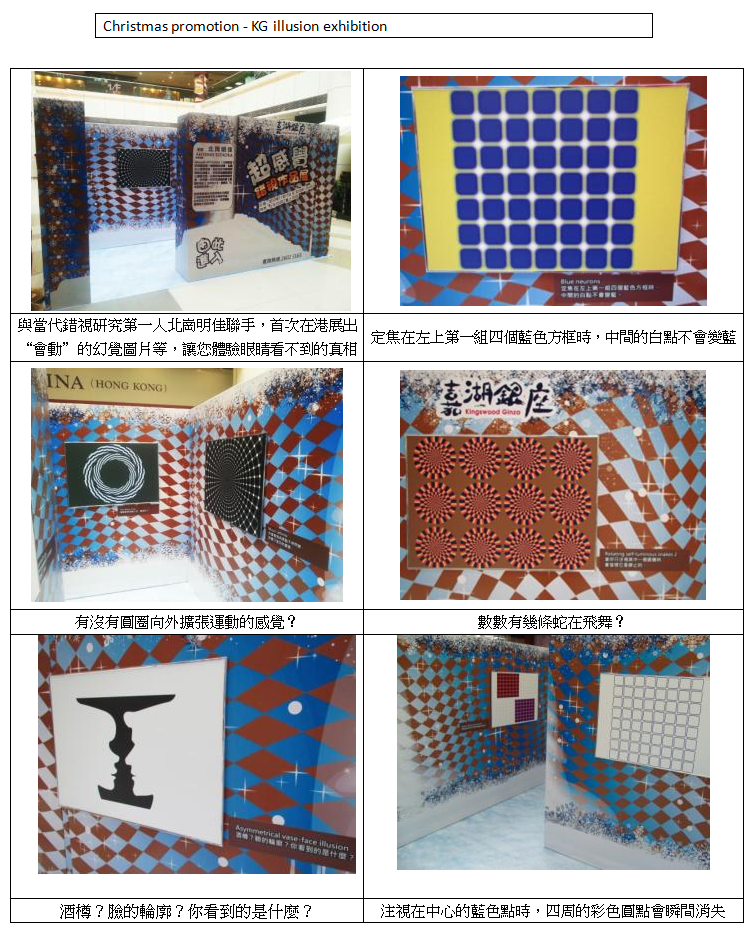

<November 14, 2012>
Professor Yanaka's study has been introduced.
Friday Illusion: Rotating snakes get a new twist
<September 24, 2012>
The result <May 15, 2012; address corrected August 22, 2012>
The Best
Illusion of the Year Contest is happy to announce that the TOP TEN illusions
have been chosen!!
The Contest Gala
will be on Monday, May 14th, 5pm, in the Philharmonic Center of Arts (Naples
Fl). The 2012 Contest Gala will be hosted by Margaret Livingstone and Stuart
Anstis! Everybody is invited!!!
Who will the TOP
THREE winners be??? That’s up to YOU! The audience will choose them from the
current TOP TEN list.
For more
details, please visit our webpage: http://illusionoftheyear.com
2012 TOP TEN ILLUSION CONTESTANTS (alphabetical
order): To see the illusions themselves… you must come to the
CONTEST!!!
"Head-Size Illusion": Kazunori Morikawa and Eri Ishii,
Osaka University, Japan
"Floating Star": Kaia Nao
"The Disappearing Hand Trick": Roger Newport, Helen Gilpin
and Catherine Preston, University of Nottingham, UK
"Exorcist Illusion – Twisting Necks": Thomas Papathomas,
Tom Grace Sr., Marcel de Heer and Robert Bunkin, Rutgers University,
USA
"Color Wagon Wheel": Arthur Shapiro and William Kistler,
American University, USA
"When Pretty Girls Turn Ugly: The Flashed Face Distortion
Effect": Jason Tangen, Sean Murphy and Matthew Thompson, The University of
Queensland, Australia
"Peripheral Action Phantom Illusion": Steven Thurman and
Hongjing Lu, UCLA, USA
"Attentional modulation of perceived color": Peter Tse,
Dartmouth College, USA
"Illusion of Height Contradiction": Sachiko Tsuruno, Kinki
University, Japan
On behalf of the
Neural Correlate Society,
Susana
Martinez-Conde (Executive Producer, Best Illusion of the Year
Contest)
Neural Correlate
Society Executive Committee: Jose-Manuel Alonso, Stephen Macknik, Susana
Martinez-Conde, Luis Martinez, Xoana Troncoso, Peter Tse
The Neural
Correlate Society is a tax-exempt 501(c)3 non-profit organization, whose mission
is to promote the public awareness of neuroscience
research.
---
Source:
<April 30, 2012>
Microsaccades and Blinks Trigger Illusory Rotation in the “Rotating Snakes” Illusion
Jorge Otero-Millan,
Stephen L. Macknik,
and Susana Martinez-Conde
Microsaccades and Blinks Trigger Illusory Rotation in the “Rotating Snakes”
Illusion
The Journal of Neuroscience, 25 April 2012, 32(17):6043-6051; doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5823-11.2012
Otero-Millan, J.,Macknik, S. L., and Martinez-Conde, S. (2012). Microsaccades and Blinks Trigger Illusory Rotation in the “Rotating Snakes” Illusion. Journal of Neuroscience, 32, 6043-6051. Jump to J. Neurosci. for PDF) -  (cover)
(cover)
<April 29, 2012>
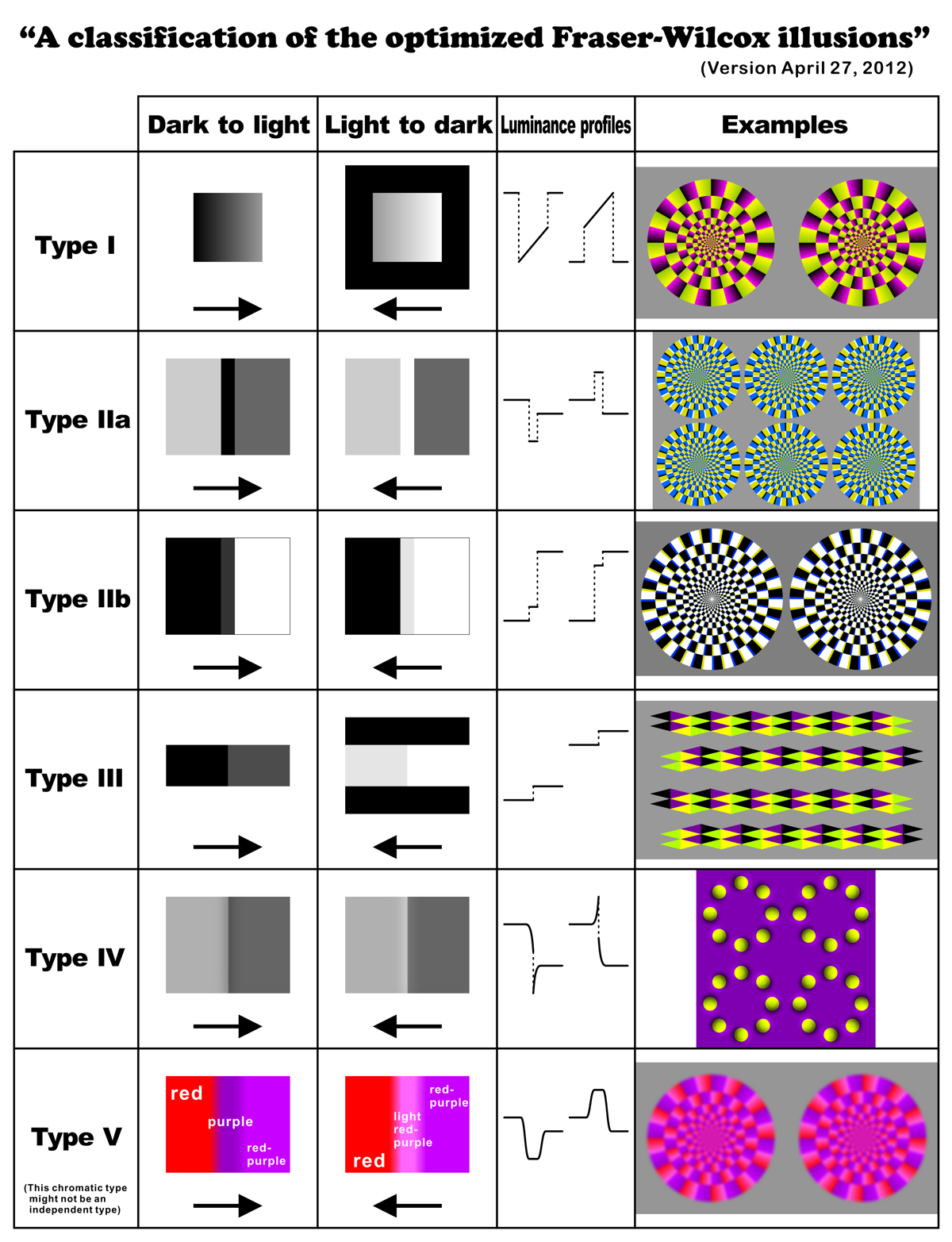
The "optimized Fraser-Wilcox" illusion (including the "Rotating snakes" illusion)
![]() Related references
Related references ![]() <before April 29, 2012>
<before April 29, 2012>
Ashida, H., Kuriki, I., Murakami, I., Hisakata, R. and Kitaoka, A. (2012 forthcoming). Direction-specific fMRI adaptation reveals the visual cortical network underlying the "Rotating Snakes" illusion. NeuroImage, in press new!
Otero-Millan, J.,Macknik, S. L., and Martinez-Conde, S. (2012). Microsaccades and Blinks Trigger Illusory Rotation in the “Rotating Snakes” Illusion. Journal of Neuroscience, 32, 6043-6051. new!
Stevanov, J., Marković, S., and Kitaoka, A. (2012). Aesthetic valence of visual illusions. i-Perception, 3(2), 112–140. PDF (i-Perception)
Yanaka, K. and Hilano, T. (2011). Mechanical shaking system to enhance "Optimized Fraser–Wilcox Illusion Type V". Perception, 40, ECVP Abstract Supplement, page 171
Tomimatsu E., Ito, H., Sunaga, S., & Remijn, G. B. (2011). Halt and recovery of illusory motion perception from peripherally viewed static images. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 73, 1823-1832.
Tomimatsu, E., Ito, H., Seno, T., and Sunaga, S. (2010). The ‘rotating snakes’ in smooth motion do not appear to rotate. Perception, 39, 721-724.
Fermüller, C., Ji, H., and Kitaoka, A. (2010). Illusory motion due to causal time filtering. Vision Research, 50, 315–329.
Scientific American Mind, Special Issue: 169
Best Illusions (2010). 
Cantor, C. R. L., Tahir, H. J., & Schor, C. M. (2010). Is the rotating snakes an optical illusion? Journal of Vision, 10(7), 824a.
Kitaoka, A. (2010). Introduction to Visual Illusions. Tokyo: Asakura-shoten, pp.110-111 (in Japanese). More info ![]()
Billino, J., Hamburger, K., & Gegenfurtner, K. R. (2009). Age effects on the perception of motion illusions. Perception, 38, 508-521.
Kitaoka, A. (2008) Trick Eyes Mechanism. Tokyo: Kanzen (in Japanese). More info ![]()
Kuriki, I., Ashida, H., Murakami, I., and Kitaoka, A. (2008). Functional brain imaging of the Rotating Snakes illusion by fMRI. Journal of Vision, 8(10):16, 1-10. PDF
Journal of Vision Volume 8, Number 10, Article 16, Pages 1-10
Functional brain imaging of the Rotating Snakes illusion by fMRI
Ichiro Kuriki
Hiroshi Ashida
Ikuya Murakami
Akiyoshi Kitaoka
http://journalofvision.org/8/10/16/
Kitaoka, A. (2008) Optimized Fraser-Wilcox illusions: A pictorial classification by Akiyoshi Kitaoka. Talk in a workshop (WS005) in the 72nd Annual Convention of the Japanese Psychological Association, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, September 19, 2008. Presentation (html)
Kuriki, I., Ashida, H., Murakami, I., and Kitaoka, A. (2008) Functional brain imaging of the 'Rotating Snakes' illusion. Vision Sciences Society Annual Meeting Abstract, Journal of Vision, 8(6),64a. http://www.journalofvision.org/8/6/64/
Hisakata, R. and Murakami, I. (2008) The effects of eccentricity and retinal illuminance on the illusory motion seen in a stationary luminance gradient. Vision Research, 49, 1940-1948.
Beer, A. L., Heckel, A. H. and Greenlee, M. W. (2008) A motion illusion reveals mechanisms of perceptual stabilization. PLoS ONE, 3(7): e2741, 1-7. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002741 Freely available online
Chi, M-T., Lee, T-Y., Qu, Y., and Wong, T-T. (2008) Self-Animating Images: Illusory Motion Using Repeated Asymmetric Patterns. ACM Transaction on Graphics (Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 2008), 27, No.3. SIGGRAPH2008 --- Authors' page --- PDF (SIGGRAPH)
Scientific American Reports Special Edition on Perception (2008). ![]()
Kitaoka, A. and Ashida, H. (2007) A variant of the anomalous motion illusion
based upon contrast and visual latency. Perception, 36, 1019-1035. ![]() PDF request to Akiyoshi Kitaoka
PDF request to Akiyoshi Kitaoka
Newton Press (Ed.), A. Kitaoka (Supervisor)
(2007) Newton magazine book: Special
issue "How is the brain deceived? Perfect demonstration of visual
illusions" Tokyo: Newton Press (in Japanese; published in October 2007). ![]()
Ramachandran, V. S. and Rogers-Ramachandran, D. (2007) A Moving Experience: How the eyes can see movement where it does not exist. Scientific American Mind, February/March, 14-16.
Kitaoka, A. (2007) Phenomenal classification of the “optimized” Fraser-Wilcox
illusion and the effect of color. Poster presentation in DemoNight, VSS2007,
GWiz, Sarasota, Florida, USA, May 14, 2007. 
Murakami, I., Kitaoka, A. and Ashida, H. (2006)
A positive correlation between fixation instability and the strength of illusory
motion in a static display. Vision Research, 46, 2421-2431. ![]() PDF request
should be sent to Dr. Murakami
PDF request
should be sent to Dr. Murakami
Kanazawa, S., Kitaoka, A., & Yamaguchi, M. K. (2006). Infants see the 'Rotating Snake' illusion. Perception, 35, ECVP Abstract Supplement.
Kitaoka, A. (2006). The effect of color on the optimized Fraser-Wilcox illusion. Paper presented for the 9th L'ORÉAL Art and Science of Color Prize, Tokyo (pp.1-16) (Gold prize was given). MS-Word manuscript (75MB)
Kitaoka, A. (2006) Anomalous motion illusion and stereopsis. Journal of Three Dimensional Images (Japan), 20, 9-14. PDF PDF (manuscript but the same as the printed one)
Kanazawa, S., Kitaoka, A. and Yamaguchi, M. K. (2006) Infants see the “Rotating Snake” illusion. Dorsal and ventral streams in the visual system (Talk): Monday, 21 August 2006; 12:00-12:30 (29th European Conference on Visual Perception, St-Petersburg, Russia, 20th-25th August, 2006) Abstract
Kitaoka, A., Ashida, H., and Murakami, I. (2005) Does the peripheral drift illusion generate illusory motion in depth? Journal of Three Dimensional Images (Tokyo), 19, 6-8. PDF (scanned copy) (poor quality) --- MS-Word file (manuscript, the same as the paper) (high quality)
Conway, R. B., Kitaoka, A., Yazdanbakhsh, A., Pack, C. C., and Livingstone,
M. S. (2005) Neural basis for a powerful static motion illusion. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 5651-5656. ![]() PDF request should be sent to Dr. Conway
PDF request should be sent to Dr. Conway
Backus, B. T. and Oruç, I. (2005) Illusory motion from change over time in the response to contrast and luminance. Journal of Vision, 5, 1055-1069. http://journalofvision.org/5/11/10/
Kitaoka, A. (2005) Trick Eyes Graphics. Tokyo: Kanzen (in Japanese and
English). More info 
Kitaoka, A. and Ashida, H. (2003) Phenomenal characteristics of the peripheral drift illusion. VISION (Journal of the Vision Society of Japan), 15, 261-262. PDF
Naor-Raz, G. and Sekuler, R. (2000) Perceptual dimorphism in visual motion from stationary patterns. Perception, 29, 325-335.
Faubert, J. and Herbert, A. M. (1999) The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery. Perception, 28, 617-621.
Fraser, A. and Wilcox, K. J. (1979) Perception of illusory movement. Nature, 281, 565-566.
 |
|
|
<March 6, 2012>
Session Name: Motion: Neural mechanisms and models (Poster session)
<February 8, 2012>
Nature, too, has highlighted this discovery! <February 2, 2012>
"Bright illusions reduce the eye's pupil"
Bruno Laeng, Professor of University of Oslo, and his colleague showed that illusions
of brightness cause constriction of the eye pupil as if the eye was exposed
to more light!
Moreover, one of the illusions they have used in this research was one
of my illusion works 'Asahi' (morning sunlight), as shown below. Thanks, Bruno!
Laeng, B. and Endestad, T. (2012). Bright illusions reduce the eye's pupil.
Proceedings of the National Acedemy of Sciences of the United States of
America (PNAS), February 7, vol. 109 no. 6 2162-2167.
http://www.pnas.org/content/109/6/2162
& ScienceShot: Brightness Is in the Eye of the Beholder

Your pupil must be constricted!
![]() Akiyoshi's further comment
Akiyoshi's further comment

This effect is kind of visual phantom illusion or Zavagno's glare effect. Note that the glare appears to be brighter at a glance than no-glare white parts, but the glare actually appears to be darker if analytically or locally (point-to-pointwise) observed, i.e. counterphase brightness induction. Thus, pupils contract in spite of dark stimuli!
Kitaoka, A., Gyoba, J., and Sakurai, K. (2006) Chapter 13 The visual phantom illusion: a perceptual product of surface completion depending on brightness and contrast. Progress in Brain Research, 154 (Visual Perception Part 1), 247-262. PDF --- Talk in ECVP2005
![]() Akiyoshi's further comment 2
Akiyoshi's further comment 2

"Evening dusk"
The illusion and title were proposed by Bruno Laeng; This image was drawn by Akiyoshi Kitaoka 2012 (January 24)
The space surrounded by 'petals' appears to be darker than the outer space, though they are the same luminance. This has been given by Bruno (Figure 1b: http://www.pnas.org/content/109/6/2162), but I have never shown such a demo. Thus, I think that the credit of this effect should be given to Bruno. Or did someone show this? If so, let me know.
<January 24, 2012>
Composites of portrait and profile (Creator: Jesús González Rodríguez) <January 27, 2012>
Nice Demos!
Flash-lag effect: Flash-lag Effect: Visual Illusion 3D (uploaded November 1, 2011 on YouTube by Professor Eiji Watanabe)
Flash-drag effect: Flash-drag Effect 3D demo (uploaded January 4, 2012 on YouTube by Professor Eiji Watanabe)
Alley experiments: Three Tokyo Sky Trees (uploaded January 4, 2012 on YouTube by Professor Eiji Watanabe)
<January 23, 2012>
Medaka (kinds of fish) see a visual illusion of prey!
Matsunaga, W. & Watanabe, E. Visual motion with pink noise induces predation behaviour. Sci. Rep. 2, 219; DOI:10.1038/srep00219 (2012). Access
<January 12, 2012>
ECVP2012
European Conference on Visual Perception | 2-6 September 2012, Alghero, Italy
VSAC2012
1st Visual Science of Art Conference | 1-2 September 2012, Alghero, Italy
<December 21, 2011>


Baingio
SfN Takemura et al. present:
Hiromasa
Takemura1,2), Hiroshi Ashida3), Kaoru Amano4,5),
Akiyoshi Kitaoka 6, 7), Ikuya Murakami1)
1) Depatment of Life Science, The University of Tokyo
2) JSPS Research Fellow
3) Graduate School of Letters, Kyoto University
4) Department of Complex Science and Engineering, The University of Tokyo
5) PRESTO, JST
6) Department of Psychology, Ritsumeikan University
7) CREST, JST
As mentioned in a previous notification, your abstract is scheduled for
Poster Session 695, Motion Processing in the Human Brain, which will
be held on Tuesday, November 15, 2011 in the Hall A-C. The session will begin at 1:00pm. Your abstract's detailed presentation
information is listed below:
Abstract
Control Number: 1647
Abstract
Title: Neural correlates of induced motion
perception in the human visual cortex
Presentation
Number: 695.05
Presentation
Time: 1:00pm - 2:00pm
Poster Board Number: NN21
<July 26, 2011>
i-PERCEPTION volume 2, issue 4
http://i-perception.perceptionweb.com/journal/I/volume/2/issue/4
Contents: Asia-Pacific Conference on Vision, Hong Kong, 2011
<July 11, 2011>
"Illusion Museum" was opened in Tokyo today!!
<May 14, 2011>
![]() A website "Test online the level of stress a person can handle using stress pictures: are they animated, moving?" abuses three of my illusion works as well as claims an unscientific idea. To my knowledge, stress has nothing to do with visual illusion. <April 25, 2011>
A website "Test online the level of stress a person can handle using stress pictures: are they animated, moving?" abuses three of my illusion works as well as claims an unscientific idea. To my knowledge, stress has nothing to do with visual illusion. <April 25, 2011>
Illusion news 14 (July 2010 - April 2011)
Illusion news 13 (September 2009 - June 2010)
Illusion news 12 (March 2009 - June 2009)
Illusion news 11 (September 2008 - January 2009)
Illusion news 10 (May 2008 - September 2008)
Illusion news 9 (February 2008 - April 2008)
Illusion news 8 (November 2007 - February 2008)
Illusion news 7 (September 2007 - October 2007)
Illusion news 6 (June 2007 - September 2007)
Illusion news 5 (January 2007 - May 2007)
Illusion news 4 (January 2006 - December 2006)
Illusion news 3 (January 2006 - May 2006)
Illusion news 2 (April 2005 - December 2005)
Illusion news 1 (2002 - March 2005)