Classification of anomalous motion illusions
This classification is not completed or is not the accepted one. This is only my tentative proposal
since August 30, 2004 updated September 7, 2006
| Type | Characteristics | Direction of illusory motion | Source of illusion | Examples | Notes |
| I | A smooth retinal slip generates this type | Perpendicular to the retinal slip | Misintegration of motion signals? | 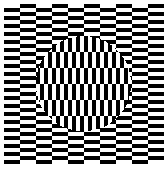 |
Ouchi illusion, Pinna-Brelstaff illusion, and others |
| II | A smooth retinal slip generates this type, where low-contrast regions appear to move | The same direction as the retinal slip | Visual latency? |  |
Kitaoka and Ashida, ECVP2002 Glasgow"An anomalous motion illusion based upon signal delay" (cf. fluttering heart) |
| III | A smooth retinal slip generates this type, where low-spatial-frequency parts appear to move | The same direction as the retinal slip | Difference in apparent speed? |  |
Kitaoka and Ashida, forthcoming |
| IV | Chromatic edges appear to move | ? | Dynamic changes in chromatic abberation? | 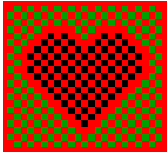 |
Kitaoka, Kuriki and Ashida, under study (cf. fluttering heart) |
| V | Staircase-shape edges appear to move | ? | ? |  |
Kitaoka (2002) Trick Eyes. Tokyo: Kanzen |
| VI | "Heat shimmer" appears | ? | ? |  |
Kitaoka (2002) Trick Eyes. Tokyo: Kanzen |
| VII | An illusory "hop" appears | ? | ? | 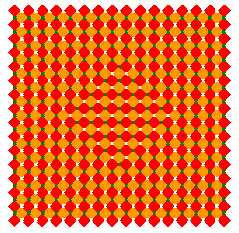 |
Kitaoka (2002) Trick Eyes. Tokyo: Kanzen |
| VIII | Parts appear to move in a constant direction | Constant | Luminance profile or luminance gradient | 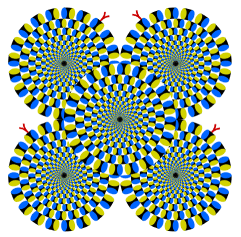 |
Optimized Fraser-Wilcox illusion Kitaoka and Ashida (2003a) |
| IX | Parts appear to move in a constant direction | Constant | Luminance gradient | 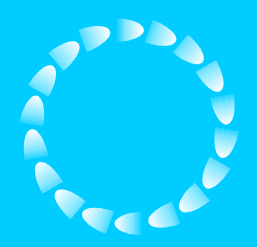 |
"Central" drift illusion Kitaoka and Ashida (2003b) |
| X | Parts appear to move in either of the two directions | Bistable | Blink-dependent apparent movement? | 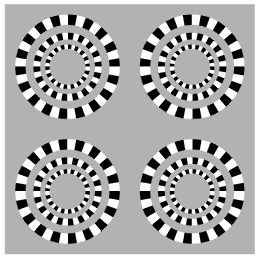 |
Blink-dependent rotation cf. Faubert and Herbert's (1999) peripheral drift illusion (this should be an independent category) |
| XI | Parts appear to move in a constant direction | Constant | Cross of lines | 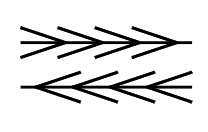 |
under study |
There are some images that cannot be classified into any of these categories.